1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import chainer.optimizers as Opt
import chainer.functions as F
import chainer.links as L
from chainer import Variable, Chain, config, cuda
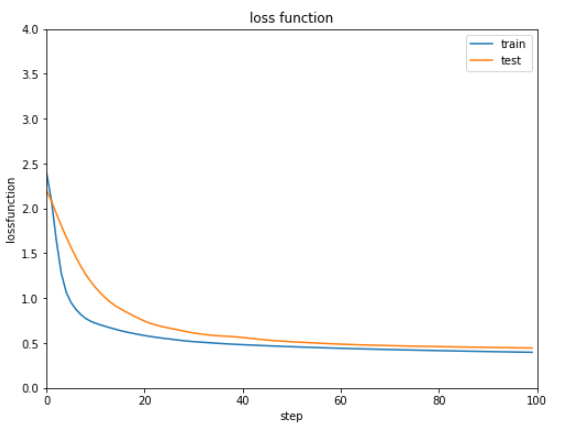
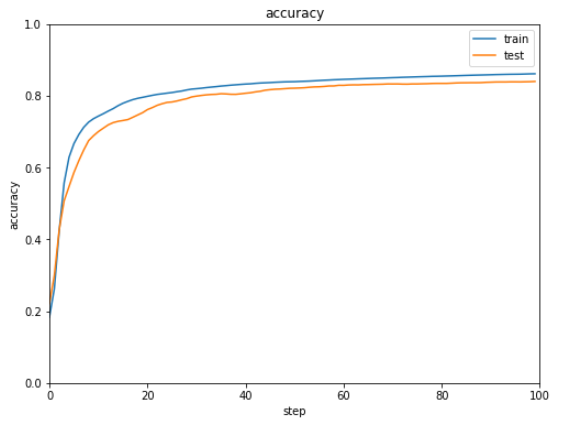
def show_graph(result1, result2, title, xlabel, ylabel, ymin=0.0, ymax=1.0):
Tall = len(result1)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(range(Tall), result1, label='train')
plt.plot(range(Tall), result2, label='test')
plt.title(title)
plt.xlabel(xlabel)
plt.ylabel(ylabel)
plt.xlim([0, Tall])
plt.ylim(ymin, ymax)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
def learning(model, optNN, data, T=10):
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_loss = []
test_acc = []
data = cuda.to_gpu(data, gpu_device)
for time in range(T):
config.train = True
optNN.target.cleargrads()
ytrain = model(data[0])
loss_train = F.softmax_cross_entropy(ytrain, data[2])
acc_train = F.accuracy(ytrain, data[2])
loss_train.backward()
optNN.update()
config.train = False
ytest = model(data[1])
loss_test = F.softmax_cross_entropy(ytest, data[3])
acc_test = F.accuracy(ytest, data[3])
train_loss.append(cuda.to_cpu(loss_train.data))
train_acc.append(cuda.to_cpu(acc_train.data))
test_loss.append(cuda.to_cpu(loss_test.data))
test_acc.append(cuda.to_cpu(acc_test.data))
return train_loss, test_loss, train_acc, test_acc
|